The Pressure Units Converter is an easy tool that lets you quickly switch between units like Pascals, bar, PSI, atmospheres, and more. It uses accurate conversion standards based on internationally recognized SI guidelines, so you can get reliable results. Just enter the value, choose your units, and the tool does the conversion. It’s helpful for students, engineers, technicians, or anyone who needs to work with pressure measurements.
Common Temperature Conversion
Below is a list of common pressure unit conversions to help you quickly compare different units that are frequently used in daily life. You’ll find examples such as 1 bar to psi, 200 psi to bar, and several other widely used conversions.
BAR to PSI
- 1 bar to psi → 14.3058 psi
- 1.5 bar to psi → 21.7557 psi
- 2 bar to psi → 29.0075 psi
- 2.5 bar to psi → 36.2594 psi
- 4 bar to psi → 58.0151 psi
- 5 bar to psi → 72.5189 psi
- 6 bar to psi → 87.0226 psi
- 7 bar to psi → 101.526 psi
- 8 bar to psi → 116.03 psi
- 11 bar to psi → 159.542 psi
- 12 bar to psi → 174.045 psi
- 20 bar to psi → 290.075 psi
- 25 bar to psi → 362.594 psi
- 35 bar to psi → 507.632 psi
- 100 bar to psi → 1450.38 psi
- 200 bar to psi → 2900.75 psi
- 300 bar to psi → 4351.13 psi
PSI to BAR
- 1 psi to bar → 0.0689476 bar
- 10 psi to bar → 0.689476 bar
- 15 psi to bar → 1.03421 bar
- 20 psi to bar → 1.37895 bar
- 30 psi to bar → 2.06843 bar
- 32 psi to bar → 2.20632 bar
- 33 psi to bar → 2.27527 bar
- 35 psi to bar → 2.41317 bar
- 36 psi to bar → 2.48211 bar
- 40 psi to bar → 2.7579 bar
- 50 psi to bar → 3.44738 bar
- 60 psi to bar → 4.13685 bar
- 120 psi to bar → 8.27371 bar
- 150 psi to bar → 10.3421 bar
- 200 psi to bar →13.7895 bar
- 300 psi to bar → 20.6843 bar
What is pressure ?
The force per unit area across which the force is distributed vertically to an object is pressure, and is represented by the letters p or P. Some everyday examples of the application of the pressure are syringe , inflating tire and another thing you did before reading this was typing on your keyboard to use our pressure calculator. The moment you pressed the key on the keyboard you applied a force over the area on the keyboard and this is the moment of creating pressure.
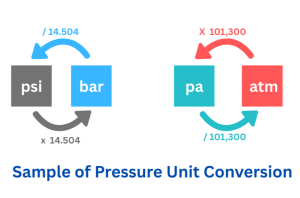
Why Converting Pressure Units Matters
Pressure plays a key role in physics, meteorology, engineering, and many industries. Different systems use different units, making it essential to convert values accurately to ensure proper measurements and comparisons. The image below illustrates a manual conversion of the units but in our Pressure Units Converter we cover this calculations for you.
Common Pressure Units
- PSI (Pounds per Square Inch): Commonly used in the US, automotive systems, and industrial tools
- Bar: Frequently used in weather data and pneumatic systems
- Pascal (Pa): The SI unit used in scientific and academic fields
- Atmosphere (atm): Based on Earth’s average air pressure at sea level
- Torr: Often used in vacuum systems and laboratory experiments
What It Does, Who It’s For, and How to Use the Pressure Unit Calculator
The main feature of the pressure unit converter is that it supports all the major unit like psi, bar, pa, atm and torr. Also it suitable for both educational and professional usage.It’s built to be useful for students, DIY users, engineers, and anyone who needs reliable pressure conversions.It takes the value you enter, applies accurate conversion factors, and instantly gives you the result in the unit you need. Whether you’re checking tire pressure, working on a school experiment, or handling technical measurements at work, the tool makes the process quick, clear, and error-free.
The Pressure Units Converter is ideal for:
- Engineers converting between pressure standards
- Students learning physics or fluid mechanics
- Technicians checking pressure values in systems
How to Use Pressure Units Converter:
- Enter the value you wish to convert.
- Select the unit you are converting from.
- Choose the unit you want to convert to.
- Click “Calculate” to view the result instantly.
Pressure Unit Conversions supported by our Converter:
- psi to bar
- psi to pa
- bar to psi
- bar to pa
- pascal to bar
- torr to atm
- torr to pa
- atm to bar
- atm to pa
- pa to psi
- pa to bar
- pa to atm
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the standard international (SI) unit of pressure?
The official SI unit of pressure is the Pascal (Pa). It simply means one Newton of force spread over one square meter.2. What is the “psi” unit usually used for?
PSI (pounds per square inch) is mostly used in the U.S. You’ll see it when checking car tire pressure, air compressors, or hydraulic tools.3. Which pressure unit is best for industrial use?
It depends on where you are and what you’re doing. PSI is common in the U.S., while industries in Europe and scientific fields usually prefer bar, kPa, or MPa because they fit the metric system.4. Can I convert pressure units to mass units, like bar to kilograms?
No, pressure and mass measure completely different things. Pressure is force over an area, while mass is just the amount of matter. Some mixed units like “kg/cm²” exist, but they’re still pressure units, not mass.5. What is the most common mistake with pressure units?
Many people mix up gauge pressure and absolute pressure. Gauge pressure starts at the air around us (atmosphere), while absolute pressure starts at a perfect vacuum. Using the wrong one can give the wrong results.6. What does “Torr” mean, and is it still used today?
A Torr is an older pressure unit equal to almost the same as mmHg (millimeters of mercury). It’s still used in vacuum systems, labs, and medical settings like blood pressure readings.Also, it named after Evangelista Torricelli.7. Why do some calculator results show a lot of decimal places?
Some conversions are very exact, so the numbers can get long. Extra decimal places help keep the results accurate, especially for scientific or engineering work.8. What is the difference between gauge pressure and absolute pressure?
Absolute pressure measures pressure starting from a perfect vacuum (zero pressure). Gauge pressure, on the other hand, measures pressure relative to the air around us. For example, when you check your car tire with a handheld gauge, you’re reading gauge pressure. A simple way to remember it: Absolute Pressure = Gauge Pressure + Atmospheric Pressure.Explore More of Our Tools
Discover additional calculators that can help you with a variety of everyday tasks and calculations. These calculators are designed to help you solve a wide range of everyday problems quickly and accurately. Our site offers a variety of helpful calculators designed to make your life easier. Click on any of the tools below to explore related calculators and discover more ways to quickly perform everyday calculations.
Temperature Converter →
Helps you to convert form units like grade Celsius, Fahrenheit and Kelvin.
Volume Units Converter →
Convert form different volume units like liter, gallon, meter cube, and more.
Area Units Calculator →
Convert form different area units like hectare, acre, meter square, and more.